Catalytic cleaning of waste gases is based on chemical transformation of toxic to non-toxic compounds in the presence of catalysts.
Application areas: neutralization of VOC, nitrogen oxides, sulfur compounds, carbon monoxide, ammonia in waste gases of industry and motor vehicles, cleaning of waste water from organic and organosulfur components.
|
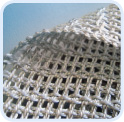
Glass-Fiber Catalysts (GFC) A low content of noble metals (0.01–0.05 wt % of platinum, palladium etc.) is characteristic of the catalyst. The catalyst is currently employed in an industrial reactor to provide neutralization no less than 99.5 % of VOC. |
|
|

|
Direct catalytic oxidation of H2S into elemental sulfur Creation of compact-size facilities for cleaning of oil associated gases from hydrogen sulfide on site of the gas extraction and treatment will result in environmental improvement owing to diminishing toxic effluents and technological waste and make it possible to bring into production suspended and proved fields of sulfurous oil. |
|
|
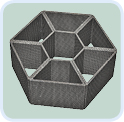 |
Structured catalytic systems based on microfiber supports A unique combination of the high catalytic activity, intense mass transfer and low pressure drop is characteristic of the structured catalytic systems. |
|
|